A Muscle Cell Experiencing Resting Membrane Potential Is
C propagating an action potential. Whilst the phenomenon of an electrical resting membrane potential RMP is a central tenet of biology it is nearly always discussed as a phenomenon that facilitates the propagation of action potentials in excitable tissue muscle and nerve.

The Mandible Human Anatomy And Physiology Bone And Joint Dentistry
Which of the following promotes the depolarization stage.

. The resting membrane potential in a muscle cell is 90 mV negative inside. The resting membrane potential in. Opening of voltage-gated sodium ion channels and sodium ions enter the cell.
Which of the following promotes the depolarization stage. These cells exhibit equilibrium potential or resting membrane potential at rest and can produce action potential during excitable. Your job is to explain to the patient how the hyperkalemia is related to their symptoms.
B The power stroke cocks the myosin head into its high-energy position. The consequence of this will be devastating for the organism in that neurons can no. A muscle cell experiencing resting membrane potential is.
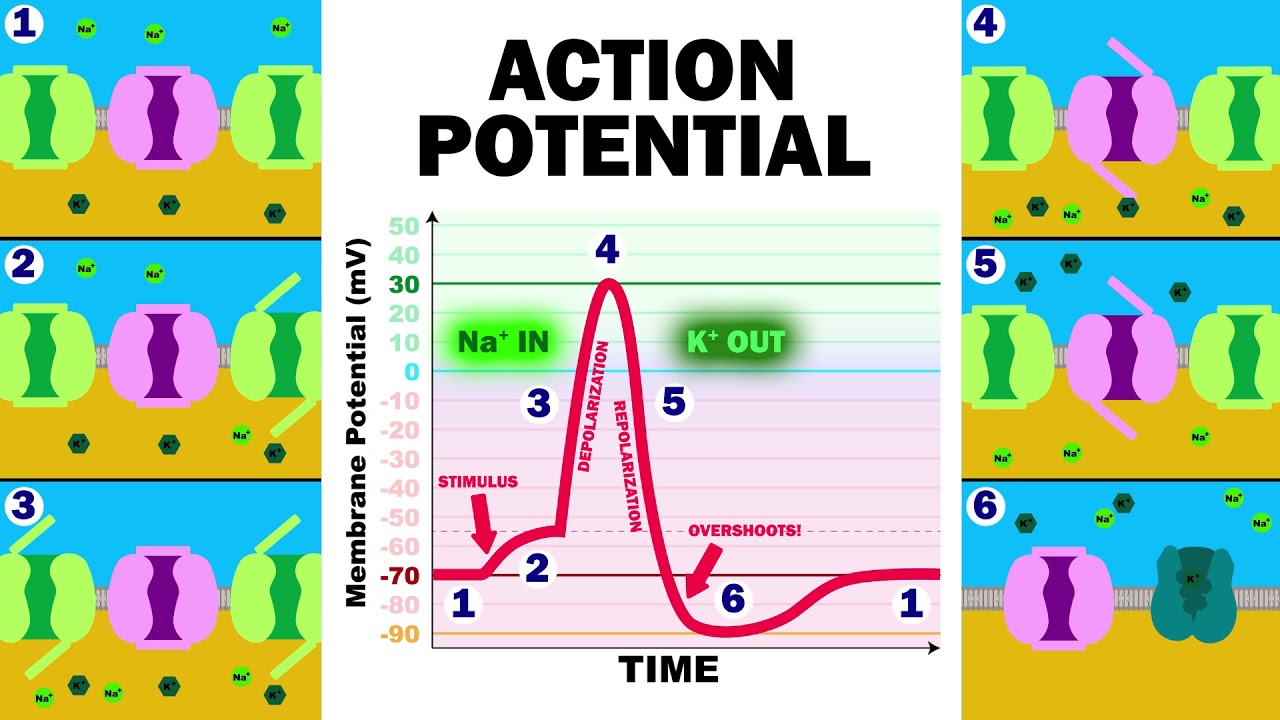
Question 18 1 1 point What does the depolarization of the transverse tubules T-tubules promote. Cytosol of the muscle cell Where should most of the potassium ions be located when a muscle cell is at rest. Therefore V m can be used to refer to the membrane potential in general and V rest can be used to refer to the resting membrane potential ie V m when the cell is at rest.
The value of RMP in nerve fibres and skeletal muscles is -90mV. A muscle cell experiencing resting membrane potential is. A muscle cell experiencing resting membrane potential is.
A resting membrane potential B action potential. The resting membrane potential RMP in neuron cells is -70mV. A resting membrane potential is the difference between the electric potential in the intracellular and extracellular matrices of the cell when it isnt excited.
Every cell of the body has its own membrane potential but only excitable cells - nerves and muscles - are capable to change it and generate an action potential. This value is close to although not the same as the equilibrium potential for K. Propagating an action potential experiencing depolarization.
The value mainly depends upon the type of the cell. In most cells examined the resting. The inside of a cell is approximately 70 millivolts more negative than the outside 70 mV note that this number varies by neuron type and by species.
Remember once a nerve cell moves away from the resting membrane potential of -70mV say toward -40mV it can send a nerve signal to muscles and cause twitching. What value best represents resting membrane potential of skeletal muscle cells-85 mV. The resting potential for a ventricular myocyte is about -90 mV which is near the equilibrium potential for K when extracellular K concentration is 4 mM.
The synapse of a motor neuron with a muscle fiber is known as the. A muscle cell experiencing resting membrane potential is. Cytosol of the muscle cell Where should most of the potassium ions be located when a muscle cell is at rest.
The reason the resting membrane potential in the muscle cell is less negative than the equilibrium potential for K is as follows. Question 17 1 1 point A muscle cell experiencing resting membrane potential is polarized more negatively charged on its exterior than its interior. The neuron cells and the muscle cells are excitable.
A neuron at rest is negatively charged. The resting membrane potential V rest refers to a situation in which the cell is at rest and no perturbations have been done to change the potential. A The power stroke allows the myosin heads to bind to actin.
A muscle cell experiencing resting membrane potential is. A muscle cell experiencing resting membrane potential is. Since the equilibrium potential for K is -96 mV and the resting membrane potential is -90 mV there is a net electrochemical driving force difference between membrane potential and equilibrium potential of 6 mV acting on.
Propagating an action potential Polarized experiencing depolarization During muscle contraction myosin bridges bind to active sites on. An action potential arrives at the axon terminal of a motor neuron 5 acetylcholine binds to ligand-gated sodium ion channels in the motor. If due to a pathophysiological condition such as elevated extracellular K levels the resting membrane potential approaches the threshold potential for neuronal and muscle voltage-gated Na channels the channels would enter the inactive state from which they cannot recover.
3 What is accomplished by the power stroke. A muscle cell experiencing resting membrane potential is. The resting membrane potential in skeletal muscle cells is -90mV.
Where should most of the potassium ions be located when a muscle cell is a rest. B more negatively charged on its exterior than in its interior. Where should most of the potassium ions be located when a muscle cell is at rest.
There exists a potential difference across the cell membrane in all the living cells in resting conditions which is known as resting membrane potential. Opening of voltage-gated sodium ion channels and sodium ions enter the cell. It is caused by differences in the concentrations of ions inside and outside the cell.
This voltage is called the resting membrane potential. The value of RMP normally varies from 5 millivolts mV to -100 millivolts mV. The NaK pump helps a muscle cell maintain a state of.
More negatively charged on its exterior than its interior. Release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum entry of sodium ions. A muscle cell experiencing resting membrane potential is.
The patient is experiencing muscle twitching due to overactive nerve fibers leading to muscles.

Muscle Twitch And Tetanus Responses Britannica

Solved Question 18 A Muscle Cell Experiencing Resting Chegg Com
0 Response to "A Muscle Cell Experiencing Resting Membrane Potential Is"
Post a Comment